In the world of precious metals, one name often stands out for its exceptional rarity and value: Rhodium. Rhodium is a silvery-white transition metal belonging to the platinum group of elements that includes platinum, palladium, ruthenium, iridium, and osmium.
Among these, rhodium holds the title of the rarest and most valuable. But what exactly is rhodium, and why is it highly prized in various industries, particularly in the automotive and jewelry sectors?
The Discovery and Properties of Rhodium
Rhodium was discovered by English chemist William Hyde Wollaston in 1803. He found it while analyzing platinum ore from South America and named it after the Greek word “rhodon,” which means rose, due to the rose-red color of the solution formed when rhodium chloride was dissolved in water.
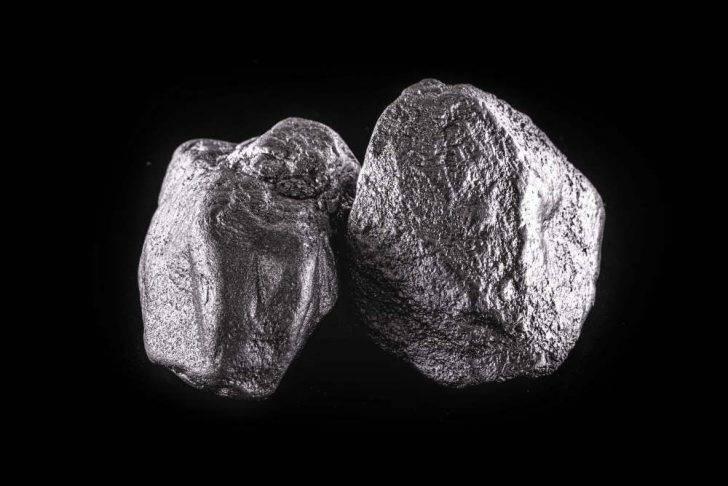

Rhodium is known for its exceptional physical and chemical properties, contributing to its high value. It has a brilliant silver-white appearance and is highly reflective, making it ideal for use in mirrors and jewelry. Moreover, rhodium is extremely corrosion-resistant, even in harsh environments, and it does not tarnish or corrode quickly, which is one of the key reasons it’s used in various applications.
Applications of Rhodium
Catalytic Converters
Rhodium finds its primary application in automobile catalytic converters, integral components within vehicle exhaust systems to minimize harmful emissions. Alongside platinum and palladium, rhodium serves as a catalyst, transforming toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides into less hazardous compounds. Its exceptional efficacy in this role is pivotal for meeting stringent global emission standards.
Electroplating
Rhodium is widely used in the electroplating industry. It is applied as a thin layer on the surface of various metals and alloys to enhance their appearance, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Jewelry, in particular, benefits greatly from rhodium plating, as it provides a lustrous, reflective finish that lasts a long time without tarnishing.

Jewelry
Rhodium’s brilliance and durability make it a sought-after choice for jewelry. It is often used to plate white gold and silver jewelry to improve their shine and prevent tarnishing. Rhodium-plated jewelry retains its luster over time, maintaining its attractive appearance without requiring frequent cleaning or maintenance.
Electronics
Rhodium is used in various electronic applications, particularly in connectors and switches. Its resistance to corrosion and electrical conductivity make it a valuable material for ensuring the reliability and longevity of electronic devices.
Aerospace
Rhodium-coated parts are used in the aerospace industry due to their resistance to extreme temperatures and environmental conditions. It finds applications in aircraft engines, sensors, and other critical components.
Medical Devices
Some medical devices, such as pacemakers and catheters, incorporate rhodium due to its biocompatibility and resistance to bodily fluids and corrosion.
Why Is Rhodium So Valuable?
Rhodium’s extraordinary value can be attributed to several factors:
Extreme Rarity
Rhodium is one of the rarest elements on Earth, with an average abundance in the Earth’s crust estimated at only 0.0002 parts per million. This scarcity places it in a league of its own among precious metals.
High Demand
The automotive industry’s growing focus on emissions reduction and stricter environmental regulations has increased the demand for rhodium in catalytic converters. Additionally, its popularity in the jewelry industry continues to drive demand.
Limited Production
Rhodium is primarily obtained as a byproduct of platinum and nickel mining. Its limited availability as a secondary product further contributes to its high market value.
Speculative Investments
The rarity and price volatility of rhodium has attracted speculative investments, which can lead to price surges in the market.

Supply Disruptions
Like many natural resources, rhodium production can be affected by supply disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and mining challenges. These factors can result in sudden price spikes.
Recycling Challenges
Unlike other precious metals, rhodium is challenging to recycle from end-of-life products due to its low concentration and the required specialized techniques. This further limits its supply.
In recent years, rhodium has experienced significant price fluctuations. From around $640 per troy ounce in 2019, its price surged to over $30,000 in early 2021, driven primarily by increased demand from the automotive industry and supply constraints. Such extreme price movements underline the speculative nature of the rhodium market.