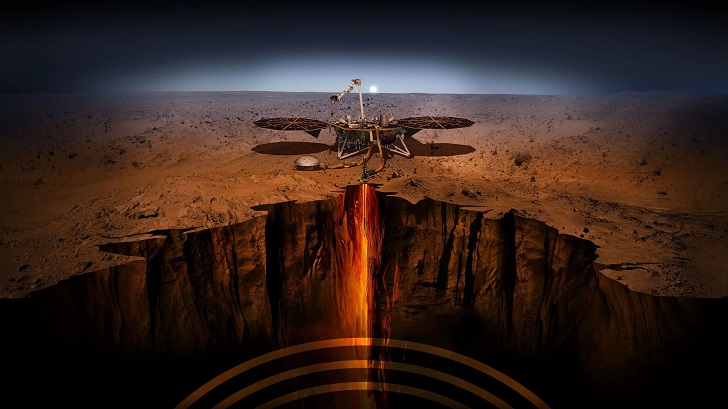
NASA’s InSight lander, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy, and Heat Transport, is a groundbreaking mission aiming to unravel Mars’ interior mysteries.
Launched on May 5, 2018, and landing on Mars on November 26 of the same year, InSight represents a significant milestone in our quest to understand the Red Planet. Below are some fascinating details of NASA’s InSight lander and its mission objectives.
Unveiling Mars’ Interior
One of the InSight mission’s primary goals is to study Mars’s deep interior, providing valuable insights into the formation and evolution of rocky planets, including Earth.
InSight carries sophisticated instruments designed to detect seismic activity, measure heat flow, and determine the planet’s wobble, shedding light on the planet’s composition and internal processes.

Seismic Investigations
InSight employs a seismometer called the Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) to study Mars’ seismic activity. This instrument is designed to detect and record marsquakes, which are seismic waves similar to earthquakes on Earth.
By analyzing these seismic waves, scientists can map the structure of Mars’ interior, including the crust, mantle, and core, and gain a deeper understanding of how the planet was formed.
Heat Flow and Geodesy
In addition to studying marsquakes, InSight also carries a heat probe called the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP^3). The probe, also known as “the mole,” is designed to burrow deep into Martian soil, measuring the planet’s internal heat flow.
Scientists can infer valuable information about the planet’s composition and thermal history by understanding how heat is conducted through Mars’ interior. Furthermore, InSight utilizes radio tracking techniques to precisely measure the lander’s location and track its movement, a process known as geodesy. This data helps scientists understand the planet’s wobble and its core size.
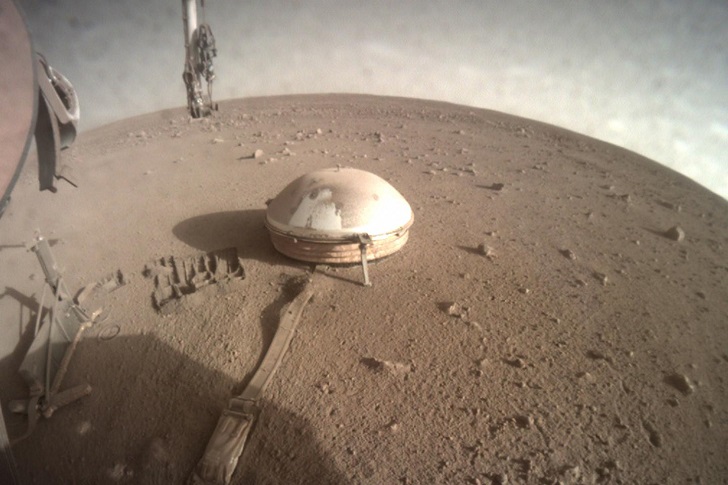

Challenges and Achievements
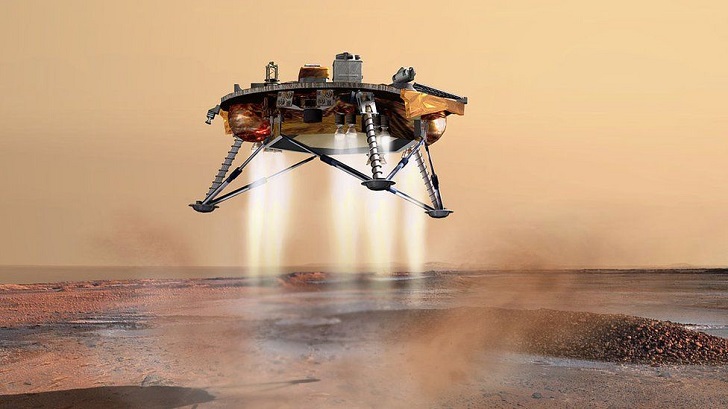
Operating on Mars presents numerous challenges, and the InSight team has overcome significant obstacles to ensure the mission’s success—one of the initial challenges involved landing the lander safely on the Martian surface.
InSight utilized a unique landing technique, combining parachutes, retrorockets, and a landing platform, to touch down in the Elysium Planitia region gently. Shortly after landing, the InSight team faced another challenge—the deployment of the heat probe.
The mole encountered unexpected resistance from the Martian soil, preventing it from burrowing to its desired depth. However, the team ingeniously devised a strategy involving the lander’s robotic arm to push against the probe, enabling it to penetrate deeper into the soil. This successful maneuver demonstrated the team’s resourcefulness and determination to overcome obstacles.

Scientific Discoveries
Since its arrival on Mars, InSight has already provided valuable scientific data. It has detected hundreds of marsquakes, ranging from small tremors to more significant seismic events.
By studying these marsquakes, scientists have mapped the structure of Mars’ interior, revealing the presence of a solid crust, a mantle with varying composition, and a large core.
Additionally, InSight has measured Mars’ vital signs, such as temperature and atmospheric pressure, providing important environmental data that contributes to our understanding of the planet’s climate and weather patterns. The lander has also detected subtle variations in Mars’ rotation, which can be attributed to mass movement within the planet.